As a system, Linux, or network administrator, you may need to use Linux high-level commands and tools to get your tasks done as quickly as possible. This article as a reference can bring happiness to your professional life with the flavor of Linux, so be prepared for some advanced Linux-based commands and tricks. This compilation is composed of many advanced and essential Linux commands and tools for professionals based on both Debian and Fedora to be of your assistance whenever possible.
More than 100 advanced Linux commands tested on Linux
A collection of high-level Linux commands within 15 different categories namely package management, Linux management, file and directory management, etc.
To begin with, Linux and its distributions based on Debian and Fedora are used and can be seen in many companies to manage their servers and services. Since the Linux operating system in nature is command-based to be utilized as much as possible, there are a plethora of standard commands and new ones in the future. Therefore, it is quite difficult to memorize all of them for our day-to-day tasks and keep pace. However, to effectively operate the Linux distributions on servers, an operator, whether an amateur or a professional, needs to frequently employ and issue as many commands as needed to keep their servers and services seamlessly running.
Considering this, this collection of Linux commands Has brought to existence to be of handy assistance to you. Also, if you are a newbie in the Linux world, I suggest checking the article on Essential Linux commands first.
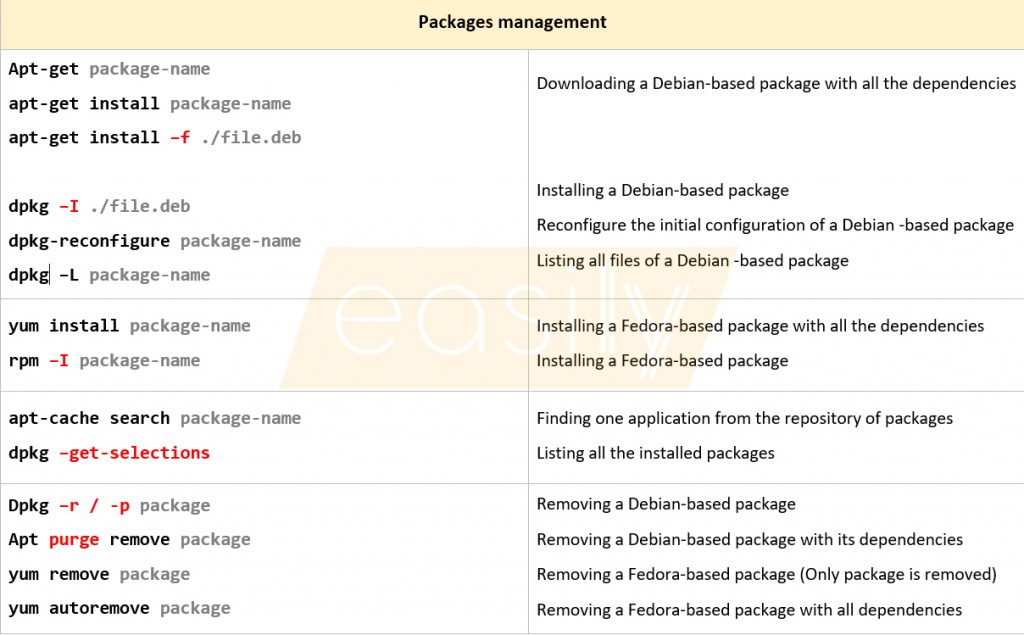
| Packages management | |
| Apt-get package-name apt-get install package-name apt-get install –f ./file.deb dpkg –I ./file.deb dpkg-reconfigure package-name dpkg –L package-name | Downloading a Debian-based package with all the dependencies Installing a Debian-based package Reconfigure the initial configuration of a Debian -based package Listing all files of a Debian -based package |
| yum install package-name rpm –I package-name | Installing a Fedora-based package with all the dependencies Installing a Fedora-based package |
| apt-cache search package-name dpkg –get-selections | Finding one application from the repository of packages Listing all the installed packages |
| Dpkg –r / -p package Apt purge remove package yum remove package yum autoremove package | Removing a Debian-based package Removing a Debian-based package with its dependencies Removing a Fedora-based package (Only package is removed) Removing a Fedora-based package with all dependencies |
| Linux management | |
| Systemctl list-unit –at service Systemctl status service-name Systemctl stop service-name Systemctl start service-name Systemctl disable service-name Systemctl enable service-name | Listing all services Showing the status of a service Making a service inactive after booting Making a service active/persistent after booting |
| pkill -KILL -u user | Logging out a user |
| hostnamectl set-hostname name | Changing the current hostname of Linux to a new one |
| Telinit 3 startx | Deactivating the X window system and going to terminal only Starting X (Graphical user interface) |
| yum update -y kernel | Updating the Linux kernel (Fedora-based) |
| Hardware management | |
| Lshw Lshw –short Lshw –html > ./hardware.html ; firefox ./hardware.html | Display the detailed information of hardware configuration |
| Dmidecode –t system | Retrieve information of a system’s hardware components |
| Dmidecode –t processor Lshw –class processor | Retrieve information of a system’s CPU |
| Dmidecode –t bios | Retrieve information of a system’s Bios |
| Lsmod Rmmode driver-name | Showing all the drivers/modules installed on a Linux’s kernel Removing a driver/module from the kernel |
| lspci | Showing all the connected devices to PCI busses |
| xdpyinfo | Displaying all the X display information |
| Free Cat /proc/meminfo Lshw –class memory | Showing the memory info of a system |
To read the rest of the article, you need to purchase and then download the ebook with the provided link below.
How to use this collection of Advanced Linux commands?
To make the most of this article, note that all the provided commands are in black color with their standard form followed by their needed options based on their purposes in red color. Further, if necessary, some commands need a file or directory name and/or an address of a file or a directory which are in gray color. Last but not least, some commands require root privilege to run. To use root privilege, su – has to be issued only if you have the password of the root of a Linux.
How to buy and download the digital file?
Easillyy works with Paypal to facilitate the transaction process. After finishing the payment process which is straightforward and can be seen on the payment guideline page, the file will be automatically sent to your email. To finish the payment process, you only need to have a valid debit or credit card and provide your details.
| Ebook | Advanced Linux commands and tools |
| File format | PDF (Digital file) |
| Version | First edition |
| Page | 19 pages |
| Price | $3 US |
| Payment method | PayPal (All credit and debit cards) |
 |

Be First to Comment